Macros defined with PyXLL can be called from Excel the same way as any other Excel macros.
Once you have written your Python function, decorated it with the xl_macro decorator, and
configured PyXLL (as described in the previous section) you are ready to
call the macro function from Excel.
Tip
Don’t forget you need to reload after making changes to your Python code or the PyXLL config!
The most usual way is to assign a macro to a control. To do that, first add the Forms toolbox by going to the Tools Customize menu in Excel and check the Forms checkbox. This will present you with a panel of different controls which you can add to your worksheet. For the message box example above, add a button and then right click and select ‘Assign macro…’. Enter the name of your macro, in this case popup_messagebox. Now when you click that button the macro will be called.
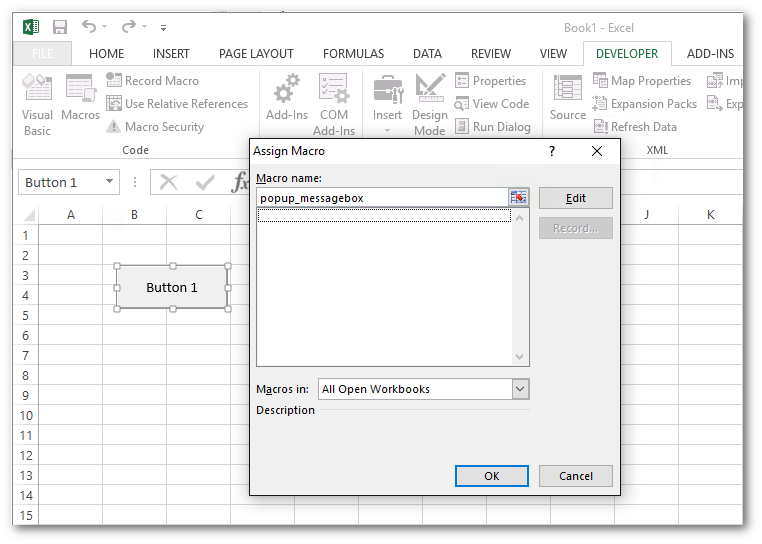
Warning
The Assign Macro dialog in Excel will only list macros defined in workbooks. Any macro defined in
Python using xl_macro will not show up in this list. Instead, you must enter the name
of your macro manually and Excel will accept it.
It is also possible to call your macros from VBA. While PyXLL may be used to reduce the need for VBA in your projects, sometimes it is helpful to be able to call python functions from VBA.
Here’s an example Python function exposed to Excel as a macro:
from pyxll import xl_macro
@xl_macro("str s: int")
def py_strlen(s):
"""Return the length of a string"""
return len(s)
For the py_strlen example above, to call that from VBA you would use the Run VBA function, e.g.
Sub SomeVBASubroutine
x = Run("py_strlen", "my string")
End Sub